Identification of Antibiotic Drugs against SARS-CoV2 Mpro: A Computational Approach for Drug Repurposing
Abstract
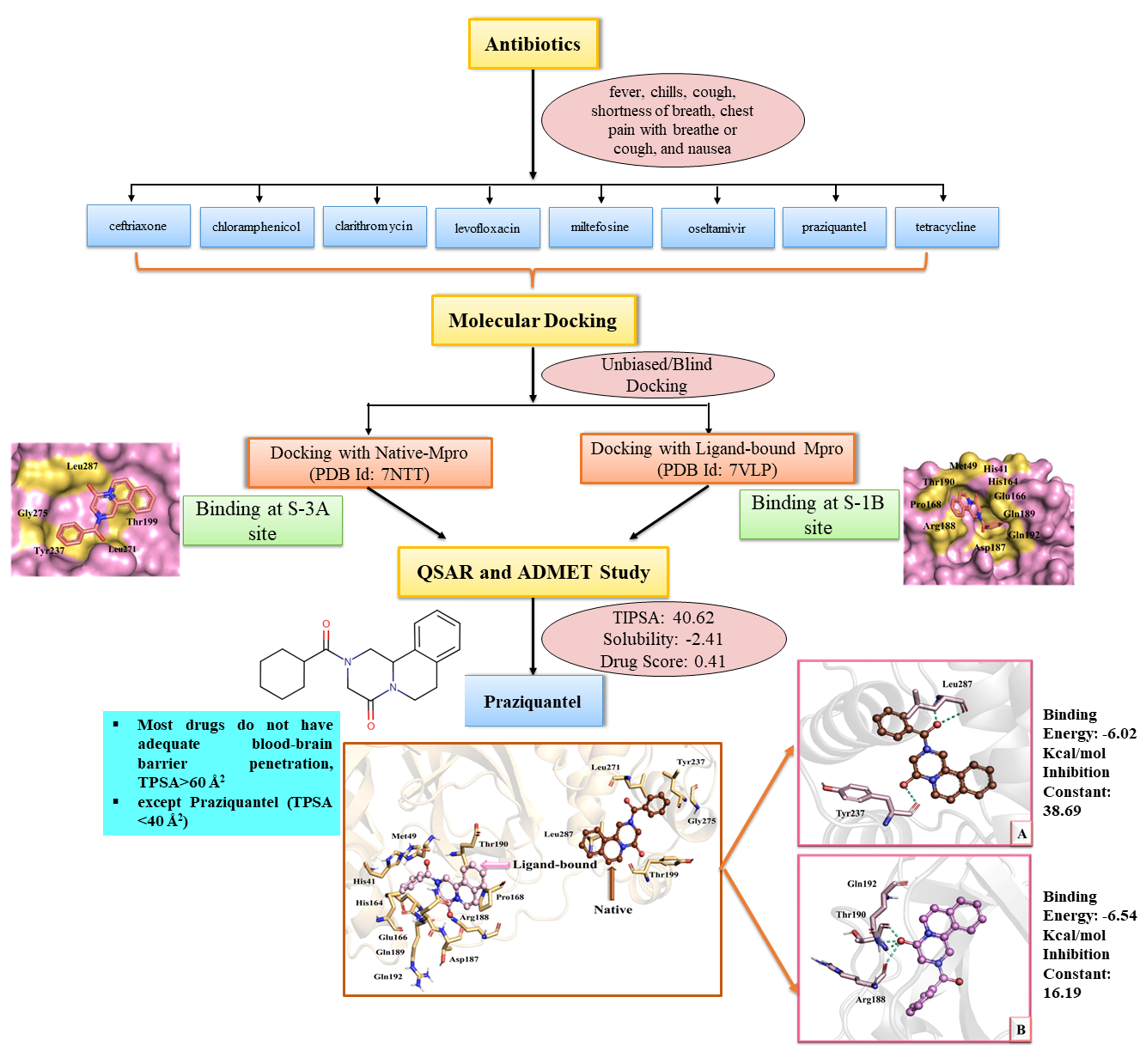
The coronavirus pandemic has posed a significant challenge for researchers seeking to develop new compounds and repurpose existing drugs to manage this disease. It has been found that the Main protease enzyme (Mpro) is critical to the replication of the virus, making it an attractive target for drug development. Different antibiotics have been proven effective against different viruses, leading to their recommendation for COVID-19.
In this study, virtual screening, pharmacokinetics, QSAR, and molecular docking techniques were used to investigate the best antibiotic drugs for COVID-19 by targeting the active and inactive conformations of the Mpro enzyme. The results of the study demonstrate that Praziquantel is a promising candidate for COVID-19 treatment. This is due to several reasons:
First, Praziquantel exhibits better binding energy in both the conformations of Mpro. Second, it binds in S-3A site in native conformation and S-1B in active state. Third, Praziquantel has excellent absorption properties, strong blood-brain barrier penetration power, and reasonably good solubility.
Therefore, the study nominates Praziquantel as the best option for future experimental and pre-clinical investigations for COVID-19.
Copyright (c) 2024 Hridoy Ranjan Bairagya, Sweety Gupta, Sayanti Pal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright © by the authors; licensee Research Lake International Inc., Canada. This open-access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (CC BY-NC) (http://creative-commons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).